|
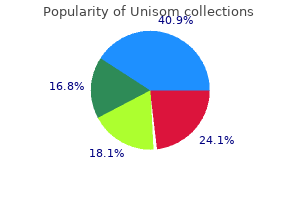
"Unisom 25 mg discount visa, insomnia ios 5". A. Yespas, M.A., M.D. Clinical Director, Harvard Medical School
As the bile flows via the biliary system of ducts, its composition could be modified within the ductules and ducts by the processes of reabsorption and secretion, particularly of electrolytes and water. For example, osmotically active compounds, together with bile acids, transported into the bile promote the passive motion of fluid into the duct lumen. In the gallbladder, composition of the bile is modified additional via reabsorptive processes. Hence, medication with molecular weights decrease than those of most protein molecules readily attain the hepatic extracellular fluid from the plasma. A number of compounds are taken up into the liver by carrier-mediated systems, while extra lipophilic medicine cross by way of the hepatocyte membrane by diffusion. The subsequent passage of gear into the bile, nevertheless, is much more selective. Compounds of group A are those whose concentration in bile and plasma are almost identical (bile�plasma ratio of 1). Group B accommodates the bile salts, bilirubin glucuronide, sulfobromophthalein, procainamide, and others, whose ratio of bile to blood is much greater than 1, normally 10 to 1,000. Group C is reserved for compounds for which the ratio of bile to blood is lower than 1, for example, insulin, sucrose, and proteins. However, biliary excretion plays a major function (5�95% of the administered dose) in drug removing for some anions, cations, and sure un-ionized molecules, corresponding to cardiac glycosides. In addition, biliary elimination could also be essential for the excretion of some heavy metals. Cardiac glycosides, anions, and cations are transported from the liver into the bile by three distinct and independent carrier-mediated lively transport techniques, the last two intently resembling those in the renal proximal tubules that secrete anions and cations into tubular urine. As is true for renal tubular secretion, proteinbound drug is totally out there for biliary lively transport. Thus, the power of certain compounds to be actively secreted into bile accounts for the big amount of those medication faraway from the body by means of the feces. The physicochemical properties of most medication are sufficiently favorable for passive intestinal absorption that the compound will reenter the blood that perfuses the intestine and once more be carried to the liver. Such recycling may proceed (enterohepatic cycle or circulation) till the drug both undergoes metabolic changes in the liver, is excreted by the kidneys, or each. This process permits the conservation of such essential endogenous substances because the bile acids, vitamins D3 and B12, folic acid, and estrogens (Table four. Orally administered activated charcoal and/or anion trade resins have been used clinically to interrupt enterohepatic biking and trap drugs within the gastrointestinal tract. As acknowledged earlier, many international compounds are either partially or extensively metabolized in the liver. Such a rise in bile secretion can cut back blood ranges of medicine that depend on biliary elimination. Finally, the administration of 1 drug may influence the rate of biliary excretion of a second coadministered compound. These results may be caused through an alteration in one or more of the next components: hepatic blood circulate, uptake into hepatocytes, rate of biotransformation, transport into bile, or fee of bile formation. In addition, antibiotics may alter the intestinal flora in such a way as to diminish the presence of sulfatase and glucuronidase-containing bacteria. This would end in a persistence of the conjugated form of the drug and therefore a decrease in its enterohepatic recirculation. Conjugation of a compound or its metabolites is very important in figuring out whether the drug will bear biliary excretion. Conjugation typically enhances biliary excretion, since it each introduces a powerful polar. Molecular weight might, nevertheless, be much less essential in the biliary excretion of natural cations. Such a steady recirculation might lead to the appearance of drug-induced toxicity. The kidney and liver are, in general, able to actively transporting the same natural anion substrates. However, the 2 organs have sure quantitative differences in drug affinity for the transporters. Liver disease or harm might impair bile secretion and thereby result in accumulation of certain medication, for example probenecid, digoxin, and diethylstilbestrol. Impairment of liver perform can result in decreased rates of each drug metabolism and secretion of medicine into bile. These two processes, of course, are frequently interrelated, since many medication are candidates for biliary secretion solely after acceptable metabolism has occurred. Decreases in biliary excretion have been demonstrated at both ends of the age continuum. This is largely because of a decreased ability of biliary secretion to remove ouabain from the plasma. Certainly, gases and other risky substances that enter the body primarily through the respiratory tract may be expected to be excreted by this route. No specialized transport techniques are concerned within the loss of substances in expired air; easy diffusion across cell membranes is predominant. Increasing cardiac output has the best impact on the removing of poorly soluble gases; for example, doubling the cardiac output almost doubles the charges of loss. Agents with excessive blood and tissue solubility, however, are only slowly transferred from pulmonary capillary blood to the alveoli. Ethanol, which has a comparatively excessive blood fuel solubility, is excreted very slowly by the lungs. The arterial focus of a extremely soluble gas falls much more slowly, and its rate of loss depends more on respiratory rate than on cardiac output. A more detailed dialogue of the uptake, distribution, and elimination of compounds administered by inhalation could be found in Chapter 25. The mechanisms involved in drug excretion are comparable for sweat and 4 Metabolism and Excretion of Drugs 45 saliva. Excretion mainly is determined by the diffusion of the un-ionized lipid-soluble type of the drug throughout the epithelial cells of the glands. Thus, the pKa of the drug and the pH of the person secretion shaped in the glands are important determinants of the whole quantity of drug showing in the specific body fluid. Lipid-insoluble compounds, corresponding to urea and glycerol, enter saliva and sweat at rates proportional to their molecular weight, presumably due to filtration by way of the aqueous channels in the secretory cell membrane. Drugs or their metabolites that are excreted into sweat could also be no less than partially responsible for the dermatitis and different pores and skin reactions attributable to some therapeutic agents. The excretion of a drug into saliva accounts for the drug taste sufferers sometimes report after certain compounds are given intravenously. The final focus of the person compound in milk will rely upon many factors, together with the amount of drug in the maternal blood, its lipid solubility, its degree of ionization, and the extent of its energetic excretion. Thus, the physicochemical properties that govern the excretion of drugs into saliva and sweat also apply to the passage of medication into milk. In distinction, the levels of weak natural acids will most likely be decrease than those in plasma. Low-molecularweight un-ionized water-soluble medicine will diffuse passively throughout the mammary epithelium and transfer into milk. There they could reside in affiliation with a number of milk parts, for example, sure to protein similar to lactalbumin, dissolved within fats globules, or free within the aqueous compartment. Compounds used in agriculture also could also be handed from cows to people by this route. Finally, antibiotics such because the tetracyclines, which can operate as chelating agents and bind calcium, have a better milk than plasma focus. In addition, composition of the milk shall be affected by the maternal food regimen; for example, a high-carbohydrate food plan will enhance the content material of saturated fatty acids in milk. The greatest drug exposure occurs when feeding begins shortly after maternal drug dosing. Additional factors determining exposure of the infant include milk quantity consumed (about a hundred and fifty mL/kg/day) and milk composition at the time of feeding. Fat content is highest in the morning after which progressively decreases till about 10 P.
Additional information:
The impact of a noncompetitive antagonist on the dose�response curve for an agonist could be the same because the effect of a non�equilibrium-competitive antagonist. The practical distinction between a noncompetitive antagonist and a nonequilibrium-competitive antagonist is specificity. The noncompetitive antagonist antagonizes agonists acting by way of a couple of receptor system; the nonequilibrium-competitive antagonist antagonizes solely agonists acting by way of one receptor system. The antihypertensive drug diazoxide is one of the few examples of therapeutically useful noncompetitive antagonists (see Chapter 20). Receptors are macromolecules that (A) Are designed to entice medication (B) Are immune to antagonists (C) Exist as targets for physiological neurotransmitters and hormones (D) Are only on the outer surface of cells (E) Are only within cells 2. Which of the next chemical bonds would create an irreversible mixture of an antagonist with its receptor Potency is decided by (A) Affinity alone (B) Efficacy alone (C) Affinity and efficacy (D) Affinity and intrinsic exercise (E) Efficacy and intrinsic activity 1. Choice A is incorrect as a end result of this mix does provoke a sign transduction course of. C and D are incorrect because each neurotransmitters and hormones work via their applicable receptor to provoke sign transduction. To be efficient, the drug should leave the vascular area and enter the intercellular or intracellular areas or both. The rate at which a drug reaches its web site of motion is dependent upon two charges: absorption and distribution. Absorption is the passage of the drug from its website of administration into the blood; distribution is the delivery of the drug to the tissues. To reach its web site of motion, a drug must cross a quantity of organic obstacles and membranes, predominantly lipid. Competing processes, corresponding to binding to plasma proteins, tissue storage, metabolism, and excretion. The pores permit the membrane to be much less restrictive to the passage of low-molecularweight hydrophilic substances into cells. In addition to its role as a barrier to solutes, the cell membrane has an essential operate in offering a structural matrix for a big selection of enzymes and drug receptors. Physicochemical Properties of Drugs and the Influence of pH the flexibility of a drug to diffuse throughout membranes is incessantly expressed by means of its lipid�water partition coefficient rather than its lipid solubility per se. This coefficient is outlined as the ratio of the concentration of the drug in two immiscible phases: a nonpolar liquid or natural solvent (frequently octanol), representing the membrane; and an aqueous buffer, normally at pH 7. The partition coefficient is a measure of the relative affinity of a drug for the lipid and aqueous phases. Increasing the polarity of a drug, both by growing its diploma of ionization or by including a carboxyl, hydroxyl, or amino group to the molecule, decreases the lipid�water partition coefficient. Alternatively, decreasing drug polarity by way of suppression of ionization or adding lipophilic. The smaller the fraction of total drug molecules ionized, the weaker the electrolyte. A smaller component consists of glycoproteins or lipoproteins which may be embedded in the lipid matrix and have ionic and polar groups protruding from one or each side of the membrane. This membrane is assumed to be capable of undergoing fast local shifts, whereby the relative geome- 20 three Drug Absorption and Distribution 21 Drug Administration. This is possible in aqueous biological techniques as a outcome of a easy mathematical relationship exists between pKa, pKb, and the dissociation constant of water pKw. Thus, understanding the pH of the aqueous medium during which the drug is dissolved and the pKa of the drug, one can, utilizing the Henderson-Hasselbach equation, calculate the relative proportions of ionized and un-ionized drug current in solution. Once a drug has been absorbed into the blood, it might be subjected to varying degrees of metabolism, storage in nontarget tissues, and excretion. The quantitative importance of each of those processes for a given drug determines the ultimate drug concentration achieved at the web site of motion. A drug is claimed to be absorbed solely when it has entered the blood or lymph capillaries. The bottom layer, which faces the cytoplasm, has a slightly totally different phospholipid composition from that of the highest layer, which faces the external medium. While phospholipid molecules can readily change laterally within their own layer, random exchange across the bilayer is uncommon. Cholesterol molecules are inclined to hold the tails of the phospholipids relatively fixed and orderly within the regions closest to the hydrophilic heads; the elements of the tails closer to the core of the membrane move about freely. These processes additionally take part in the transport of gear needed for cellular upkeep and development. Passive Diffusion Most medicine move via membranes by passive diffusion (down their focus gradient) of the unionized moiety. The fee of diffusion relies upon primarily on the lipid�water partition coefficient rather than on lipid solubility per se. For instance, the central nervous sys- three Drug Absorption and Distribution 23 tem depressant barbital is nearly utterly un-ionized at physiological pH and therefore ought to be ready to cross membranes simply. A drug will accumulate within the membrane till the ratio of its focus in the membrane and its focus in the extracellular fluid equal its partition coefficient. A concentration gradient is thereby established between the membrane and the intracellular space; this gradient is the driving drive for the passive transfer of the drug into the cell. Thus, a drug that has a very high lipid�water partition coefficient could have a big focus gradient, and this favors its speedy diffusion across the membrane and into the cell. In biological methods, the passage of many small water-soluble solutes through aqueous channels within the membrane is completed by filtration. The hypothetical diameter of those pores is about 7 �, a dimension that typically limits passage to compounds of molecular weight lower than a hundred. Facilitated Diffusion the transfer of drugs by facilitated diffusion has lots of the characteristics related to active transport, together with being a protein carrier�mediated transport system that shows saturability and selectivity. It differs from active transport, however, in that no vitality enter is required past that essential to preserve regular cellular function. In facilitated transport the motion of the transported molecule is from areas of upper to areas of decrease concentrations, so the driving drive for facilitated transport is the focus gradient. Bulk Flow Most substances, lipid soluble or not, cross the capillary wall at rates that are extraordinarily fast as compared with their charges of passage across other body membranes. In reality, the provision of most medication to the varied tissues is limited by blood move quite than by restraint imposed by the capillary wall. Active Transport the energy-dependent motion of compounds across membranes, most frequently towards their concentration gradient, is referred to as active transport. This transport entails the reversible binding of the molecule to be transferred to a membrane component (a carrier) of complementary configuration. One transport mannequin proposes that the drug molecule combines with a selected cell carrier. The complicated formed diffuses throughout the membrane to the alternative facet, the place the complex dissociates, thus releasing the drug into the aqueous compartment bordering the opposite membrane floor. Another model involves a chainlike arrangement of sites in transport channels to which the drug can bind. The drug can be transferred from one web site to another till it had traversed the membrane. The number of molecules transported per unit of time will reach a most (Tm) once the binding capacity of the service turns into saturated. Drugs corresponding to levodopa (for parkinsonism) and methyldopa (for hypertension) are actively transported. These compounds are known to penetrate the lipid membrane despite their low lipid�water partition coefficients. Endocytosis Endocytosis involves the cellular uptake of exogenous molecules or complexes inside plasma membrane� derived vesicles. This course of can be divided into two major classes: (1) adsorptive or phagocytic uptake of particles which were bound to the membrane surface and (2) fluid or pinocytotic uptake, in which the particle enters the cell as part of the fluid phase. The solute inside the vesicle is released intracellularly, possibly by way of lysosomal digestion of the vesicle membrane or by intermembrane fusion. Although the surface space of the oral cavity is small, absorption can be rapid if the drug has a excessive lipid�water partition coefficient and due to this fact can readily diffuse via lipid membranes.
Ibuprofen is contraindicated in patients with aspirin sensitivity leading to bronchiolar constriction and in sufferers with angioedema. They are analgesic, antipyretic, and antiinflammatory brokers indicated for gentle to moderate pain, remedy of dysmenorrhea, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis. These medication are metabolized via glucuronidation in the liver and excreted via the kidney. Thus, fenamates require regular liver and kidney operate for excretion and are contraindicated in sufferers with both liver or renal failure. Overdose with fenamates leads to seizures which are generally insensitive to traditional treatment with benzodiazepines. In circumstances of overdose with meclofenamate dialysis may be required to restore fluid and electrolyte stability. Their use is accompanied by critical opposed reactions, such as anemia, nephritis, renal failure or necrosis, and liver harm. Interactions with a giant number of other medicine Arylpropionic Acid Derivatives Chemistry and Mechanism of Action Ibuprofen (Advil), flurbiprofen (Ansaid), fenoprofen (Nalfon), ketoprofen (Orudis), and naproxen (Naprosyn) are all 2-substituted propionic acid derivatives. The drug is contraindicated in kids and in the elderly with diminished renal perform. The penalties of overdose occur slowly and might include liver harm, renal failure, and shock. Supportive measures include air flow, dialysis, and gastric lavage with activated charcoal, in addition to the use of benzodiazepines to management convulsions. Oxicam Derivatives Piroxicam (Feldene) is the prototypical oxicam by-product, with analgesic, antipyretic, and antiinflammatory properties. Its lengthy half-life (45 hours) favors compliance, since just one dose per day is given. Indications for the drug embrace rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and ophthalmic inflammation (use of an ophthalmic preparation). Its efficacy is equal to that of low doses of morphine in the control of ache. However, some evidence exists that ketorolac might stimulate the discharge of endogenous opioids as a part of its analgesic activity. However, tolmetin is best tolerated than aspirin and produces less tinnitus and vertigo. Tolmetin is an alternative to indomethacin in indomethacin-sensitive sufferers and is unique among such medication in that it might be used to treat juvenile arthritis. Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Uses Celecoxib has been approved for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and rofecoxib has been accredited for the therapy of osteoarthritis, acute ache and primary dysmenorrhea. Therefore, celecoxib and rofecoxib can delay in wound therapeutic and improve the time for ulcer restore and tissue regeneration. Patients with gastric ulcers Miscellaneous Agents Oxaprozin (Daypro) has pharmacological properties that are much like these of different propionic acid derivatives. However, it has a very long half-life (more than forty hours) and therefore could be effective with once-a-day treatment. Acetylation of the hydroxyl groups results in the synthesis of heroin (diacetylmorphine), R3 17 which has a much greater capacity to move the blood-brain barrier. Others contend that heroin produces analgesic effects distinct from the conversion to morphine and thus must be considered as a therapeutically helpful analgesic. Protection of that group with a methyl group, as occurs in codeine and different codeine derivatives such as oxycodone, renders the molecule less vulnerable to glucuronidation and reduces the first-pass effect within the liver. However, the glucuronidation of morphine at the hydroxyl moiety on C6 results in an energetic metabolite, morphine-6-glucuronide, which contributes to the exercise of morphine and extends its length of action. Endogenous Opioids the endogenous opioids are naturally occurring peptides that are the products of 4 known gene households. The gene liable for the production of the endomorphins, a new class of endogenous opioids, has but to be identified. The enkephalins, the first opioid peptides identified, have been first found in the brain and were therefore given the name enkephalin, which suggests from the top. The dynorphins have been so named because they have been thought to be dynamic endorphins, having a variety of actions within the body, a hypothesis that has proved to be accurate. The endogenous opioids have been implicated in the modulation of many of the important functions of the physique, together with hormonal fluctuations, thermoregulation, mediation of stress and anxiousness, production of analgesia, and improvement of opioid tolerance and dependence. As such, the endogenous opioids are crucial to the upkeep of well being and a sense of well-being. Recently, a variety of beforehand hypothesized opioid receptors have been cloned (, and). The -receptor, once thought to be an opioid receptor, is a nonopioid receptor that mediates a variety of the dysphoric results of the opioids. The cloned opioid receptors are members of the large superfamily of G protein�coupled receptors. It has been shown that 1-receptors mediate the analgesic and euphoric effects of the opioids and physical dependence on them, whereas 2-receptors mediate the bradycardiac and respiratory depressant effects. Three -opioid receptors have been recognized and are thought to mediate spinal analgesia, miosis, sedation, and diuresis. Other ascending tracts with high ranges of binding embrace the spinothalamic tracts to the subcortical areas and limbic areas of the brain responsible for the discriminative and sensory elements of pain and the euphoric effects of the drugs. Limbic areas, including cortical websites and the amygdala, are involved within the anxiolytic results of the medicine. Binding within the hypothalamus is linked to the modulation of hormone release and to thermoregulation by the opioids and opioid peptides. Some descending pathways possess excessive levels of opioid receptors believed to be linked to the analgesic effects of the drugs. In addition, the receptor binding in medullary pathways has been linked to inhibitory neurotransmitter release within the dorsal horn. Opioid binding at medullary websites is consistent with the respiratory depressant results of the medicine. Binding in the nucleus accumbens and the resultant release of dopamine by the - and -opioids is linked to the development of bodily dependence. However, the -opioids, which also bind extensively within the nucleus accumbens, are linked to a lower in dopamine launch, probably explaining their decrease abuse legal responsibility. The localization of various receptor subtypes inside different-size fiber pathways has been established. The - and -receptors seem related to the large-diameter fibers, whereas the -receptors appear to be positioned within the small to medium-size fiber bundles of the dorsal root ganglia. Such variations might clarify the modulation of particular types of nociceptive stimuli by the different opioid agonists and opioid peptides. As described beforehand, the first-pass effect on medication like morphine, which have a free hydroxyl group in position 3, is glucuronidation by the liver. In the case of morphine, the conjugation to glucuronide decreases the oral bioavailability of the drug. Following absorption, the medication distribute rapidly to all tissues, although the distribution is restricted by their lipophilicity. Fentanyl (highly lipophilic) distributes to the mind rapidly but in addition remains in fat, which serves as a slow-releasing pool of the drug. Certain of the medication, notably methadone and fentanyl, have long half-lives inconsistent with their period of motion. This discrepancy is as a result of of accumulation in numerous tissue and plasma reservoirs and redistribution from the mind to these reservoirs. Codeine passes into the brain extra readily than morphine, which is slow in crossing the blood-brain barrier. The drugs cross readily into fetal tissues across the pla- 26 Opioid and Nonopioid Analgesics 319 centa and subsequently should be used with care during pregnancy and supply. Moreover, glucuronidation by the fetus is gradual, growing buildup of the medicine and growing their half-life in the fetus. The majority of their metabolites are inactive with a couple of notable exceptions, similar to morphine-6-glucuronide, which produces an analgesic impact; normeperidine and norpropoxyphene, which produce excitatory however not analgesic results; and 6- -naltexol, which is less energetic than naltrexone as an antagonist however prolongs the motion of naltrexone. Excretion of the metabolites requires adequate renal function, since excretion by routes aside from the urine are of minor significance. Patients turn out to be inattentive to the painful stimuli, less anxious, and extra relaxed. In addition, opioids depress polysynaptic responses but can improve monosynaptic responses and lead to convulsant results in high doses. In sufferers with persistent pain, the euphoric impact of opioids, mediated by the -receptor, is normally blunted.
It has the benefit of not being pungent, a attribute that permits a clean inhalation induction, and is particularly useful in pediatric anesthesia. Hypotension is produced by sevoflurane as systemic vasodilation happens and cardiac output decreases. The degradation product from the absorbent has been reported to be nephrotoxic, although the report is controversial and not substantiated by newer research. Deep ranges of anesthesia are unattainable, even when utilizing the best practical concentrations of N2O (N2O 60�80% with oxygen 40�20%). If the airway is unprotected, vomiting might result in aspiration pneumonitis, for the rationale that protective reflexes of the airway are depressed. Such low impressed concentrations of N2O are used in dentistry and infrequently for selected painful surgical procedures. The most common use of N2O is in combination with the stronger unstable anesthetics. It decreases the dosage requirement for the other anesthetics, thus reducing their cardiovascular and respiratory toxicities. For instance, an appropriate anesthetic upkeep tension for N2O and halothane would be N2O 40% and halothane zero. With this mixture in a healthy affected person, anesthesia is sufficient for major surgical procedure, and the dose-dependent cardiac results of halothane are reduced. Earlier agents, ether and cyclopropane, have fallen out of favor, since they present a critical security hazard due to their flammability and explosiveness. They remain interesting from a historical point of view, since they had been among the many first developed. Among the earliest proposals to clarify the mechanism of action of anesthetics is the idea that they interact physically somewhat than chemically with lipophilic membrane parts to trigger neuronal failure. Nitrous Oxide: An Inhalational Gas N2O (commonly called laughing gas) produces its anesthetic impact without decreasing blood strain or cardiac output. Although it immediately depresses the myocardium, cardiac melancholy is offset by an N2O� mediated sympathetic stimulation. Tidal quantity falls, however minute air flow is supported by a centrally mediated increase in respiratory fee. Also, anesthesia produced at ambient atmospheric stress may be attenuated by bodily raising the strain to one hundred atm, a phenomenon generally recognized as strain reversal. Membrane conformational changes are noticed on exposure to anesthetics, further supporting the importance of physical interactions that lead to perturbation of membrane macromolecules. For instance, exposure of membranes to clinically related concentrations of anesthetics causes membranes to expand beyond a important volume (critical volume hypothesis) related to normal cellular function. Also, anesthetics enhance different processes recognized to inhibit neuronal perform, such as the glycine receptor�gated chloride channel. In addition, some inhalational medication activate K channels and so contribute to hyperpolarization and lowered neuronal excitability; they also inhibit the operate of the protein advanced involved in neurotransmitter release. Although bodily interactions of anesthetics with hydrophobic membrane elements may result in conformational modifications that alter neuronal perform, particular interactions at critical receptors and ion channels are additionally more likely to contribute to anesthesia. Thus, structurally and pharmacologically various anesthetic medicine produce unconsciousness through qualitatively totally different mechanisms and through actions occurring at anatomically distinct sites within the nervous system. A hypotensive affected person suspected of getting inside bleeding is given a dose lower than the identical old amount of an intravenous anesthetic. How is it potential to obtain anesthesia in this patient with a dose of anesthetic that may be inadequate in a normotensive affected person with sufficient blood quantity With which hypothetical anesthetic would you expect anesthetic partial strain to be achieved comparatively rapidly Patients with coronary artery illness are notably challenging for anesthesia, since alterations in vascular responsiveness and myocardial function may put them at risk. In this respect, which statement accurately describes the cardiovascular action of an agent or brokers that must be taken under consideration when planning anesthesia for such sufferers Which statement greatest describes important developments on this space of scientific investigation Unless supplemented with robust analgesic medication such as opioids, most basic anesthetics enable reflex reactions to painful stimuli, which may include movement and autonomic reflex changes. To give this affected person a neuromuscular blocking agent without initially evaluating the adequacy of anesthesia could be a mistake. A lawsuit is kind of certain, ought to the patient be inad- equately anesthetized and complain postoperatively of being conscious but paralyzed. Morphine may be an affordable complement to anesthetic administration to inhibit reflex reactions to noxious stimuli. Raising the impressed concentration of isoflurane could further blunt reflex reactions to noxious stimuli. The gut is sort of aware of noxious insult, however the reflex responses are still inhibited with proper analgesics, so muscular movement is avoidable. Also, since circulate to tissues associated with redistribution of the drug and termination of anesthesia is compromised, anesthesia should be deep and prolonged. While poor perfusion of the liver may scale back the publicity of medication to metabolic enzymes, most intravenous anesthetics rely very little on hepatic clearance to terminate the anesthetic impact when a single bolus is administered. Anesthetics with low blood and tissue solubility require minimal uptake from the lung, as alveolar partial pressure equilibrates with tissue. Remember, alveolar partial pressure is the driving force to set up tension gradients all through the physique. Thus, when uptake is low and alveolar rigidity rises quickly, blood and mind (which receives a high blood flow) equilibrate with gaseous agents shortly, and anesthesia is induced relatively quickly. An agent with a excessive Ostwald solubil- 25 General Anesthesia: Intravenous and Inhalational Agents 309 ity coefficient is among the more soluble brokers in tissue, so the reason of option A applies. Option E has no obvious bearing on the speed of rise of the alveolar partial stress in mind, alveolus, or any other tissue. Remifentanil has turn out to be in style as a element drug in the technique of whole intravenous anesthesia as a consequence of this characteristic. Phenylpiperidines as a category of opioids are much less more likely to produce histamine release. Chest wall rigidity is related to excessive doses of phenylpiperidine opioids specifically, and no evidence means that remifentanil could be any much less more probably to trigger such an impact. Reduced peripheral vascular resistance happens with most halogenated hydrocarbons, and reflex tachycardia could also be a priority. Halothane may be the clearest exception, since there seems to be a steadiness between rest and constrictor influences in numerous vascular beds with this agent so that complete peripheral resistance modifications very little. Halothane is the agent of concern when sensitization of the myocardium to catecholamine-induced arrhythmias could additionally be essential, corresponding to during incidences of hypercapnia. In reality, this might be a bonus of the drug in physiologically dangerous patients when swings in blood pressure are likely to be frequent. Although few contend that a unitary hypothesis will explain anesthesia, the Meyer Overton rule was among the many first explanations provided by the scientific community. The correlation stays important, because it means that websites of action for varied anesthetics may reside near (or the agent must move though) hydrophobic tissue components. Also, physical disruption of membrane perform may yet be found to play a job for no much less than some agents. Enantiomers, which have practically similar bodily properties but completely different potencies, challenge the Meyer Overton rule. Case Study Bradycardia and -Blockers A 77-year-old man is admitted to the hospital for a coronary artery bypass. He has been handled with a -blocker (Tenormin a hundred mg per day), which he took every morning. He is induced with propofol 1 mg/kg, fentanyl 5 g/kg and vecuronium 8 mg for muscle leisure. The potent opioids in the fentanyl family all trigger vagal transmitted bradycardia. The muscle relaxant vecuronium (norcuron) has no impact on heart fee and will have been replaced by pancuronium, which has a vagolytic impact and can counter bradycardia within the ordinary induction bolus doses. The stress response to pain can alter the healing process by evoking massive sympathetic discharge that in turn alters blood flow, tissue perfusion, and immune operate. In addition, in sure painful conditions the affected person has lowered respiratory perform. Hence, the time period ache, derived from the Latin poena for punishment, reflects the deleterious results that might be inflicted upon the physique. Since hundreds of thousands of Americans endure from some form of pain annually, ensuing within the expenditure of billions of dollars for varied treatment modalities, pain and its underlying causes are a significant public well being drawback.
|
|