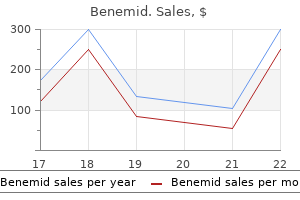
Buy benemid 500mg on-linePatients receiving intravenous therapy also wants to receive an intravenous infusion of dextrose heel pain treatment video benemid 500mg visa. The remedy for hypoglycemia is a sluggish bolus of intravenous dextrose adopted by a continuous infusion elbow pain treatment bursitis order 500mg benemid with mastercard. Hemolytic uremic syndrome has additionally been described in affiliation with quinine use (Gottschall et al pain treatment of herpes zoster benemid 500 mg purchase without prescription. In one case report, the spreading of antibody specificity from platelet to white cells and endothelium resulted in the development of thrombocytopenia to hemolytic uremic syndrome (Glynne et al. Neurologic toxicity Quinine might unmask or exacerbate myasthenia gravis (Bateman and Dyson, 1986; Karbwang et al. Indeed, quinine was as soon as used within the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis (Harvey and Whitehill, 1937; Eaton, 1943). Studies have instructed that at low concentrations quinine has a presynaptic motion to inhibit acetylcholine manufacturing or release, and at greater concentrations has an impact on postsynaptic receptors (Kornfeld et al. Rash Urticaria is the most typical rash related to quinine, however more severe dermatologic phenomena have also been described, together with erythema multiforme, mounted drug eruptions, and poisonous epidermal necrolysis (Callaway and Tate, 1974; Jarratt and Rudolph, 1975; Bateman and Dyson, 1986). Risks in pregnancy the risks of using quinine in being pregnant must be weighed in opposition to the known deleterious results of malaria on being pregnant and the risks and availability of options such as artesunate (see Chapter 169, Artemisinins). Some, however not all, animal research demonstrated abnormalities of the inner ear, the auditory nerve, and central nervous system (West and Wichita, 1938; Tanimura, 1972; Colley et al. At excessive doses, quinine has been used to induce abortion and augment labor (Dilling and Gemmell, 1929; Stirling and Hodge, 1961). As famous earlier, in pregnant women with extreme malaria, hypoglycemia appears to be a common complication of quinine therapy (Looareesuwan et al. In addition, blackwater fever has been described after treatment with artemisinin derivatives (Price et al. Quinine has been demonstrated to cause hemolysis in vitro, an impact that appears to be a result of a direct effect on red cell membranes (Bennett and Desforges, 1967). Thrombocytopenia after publicity to quinine was first described in 1865 (Vipan, 1865), and quinine use is still thought to be the most common cause of drug-induced thrombocytopenia (Aster and Bougie, 2007). Even the small amounts of quinine current in tonic water could additionally be enough publicity to induce thrombocytopenia ("cocktail purpura") (Belkin, 1967). Quinine-induced thrombocytopenia is associated with the 3066 Quinine and Quinidine Quinine crosses the placenta (cord plasma/maternal plasma ratio = 0. In research in settings exterior Southeast Asia, combining a 3-day course of quinine with a 7-day course of an anti-malarial antibiotic has been evaluated (Barata et al. A systematic evaluate of research of quinine�clindamycin combos versus quinine monotherapy identified seven scientific trials (Lell and Kremsner, 2002). Together, they recommend that shorter programs of as brief as three days of the mixture could also be efficacious in African youngsters with uncomplicated malaria (based on surrogate medical and parasitologic endpoints), however that 7 days of the mixture are required in Thai patients with uncomplicated malaria. Few studies have examined short-course therapy in extreme malaria, however in a single small research, fever clearance instances and parasite clearance times have been shorter amongst Gabonese youngsters with severe malaria handled with quinine�clindamycin for 4 days than in these treated with quinine for 7 days (Kremsner et al. In several studies, the mix of quinine with tetracycline has been examined. Short-course quinine�doxycycline regimens have been used efficiently in nonpregnant adult patients with uncomplicated malaria in Gabon (Metzger et al. The major remaining role of quinine in the therapy of malaria is as second-line therapy where price and availability limit the provision of artemisinins. It is necessary to notice that the majority efficacy studies of quinine for uncomplicated malaria have concerned supervised remedy. In studies of supervised-dosing quinine monotherapy in areas where resistance was known to be present, therapy was associated with excessive treatment charges (although lower than with quinine�antibiotic combinations) (Pukrittayakamee et al. Field effectiveness of unsupervised quinine regimens has been documented at rates as little as 11�20% regardless of well being promotion programs (Denis, 1998; Ratcliff et al. The standard dose of quinine for uncomplicated malaria is 10 mg of salt per kilogram every 8 hours for 7 days. Current recommendations recommend combining this with a 7-day course of an anti-malarial antibiotic (see later). The efficacy of rectal quinine has been examined in a number of studies in African youngsters with uncomplicated malaria. In a meta-analysis, five trials (227 children) had been identified that compared intrarectal with intravenous quinine, and three trials (1122 children) had been recognized that compared intrarectal with intramuscular quinine (Eisenhut and Omari, 2005). Comparative randomized controlled trials of antibiotic�quinine mixtures in uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Treatment arms Q7: quinine intravenously (3 days) + quinine orally (4 days) Q3C3: quinine intravenously (3 days) + clindamycin intravenously (5 mg/kg each 8 h; three days) Q7C7: quinine (10 mg salt/kg every 8 h) + clindamycin (5 mg/kg every eight h) for 7 days A7: artesunate 2 mg/kg/day for 7 days Q7: 13% (n = 53) at 28 daysa Q7T7: 0% (n = 60) Q7C7: 2. Clinical makes use of of the drug 3067 b Reinfection excluded by follow-up in no-transmission setting. Two small studies have evaluated the mix of quinine with azithromycin for the remedy of uncomplicated malaria. In a comparative trial in Thailand, fever clearance and parasite clearance occasions have been similar with 3- and 5-day quinine�azithromycin (500 mg twice per day or thrice per day) mixtures, in contrast with the usual 7-day quinine�doxycycline mixture (Miller et al. In one other small trial of a 3-day quinine�azithromycin routine (500 mg 3 times per day or 750 mg twice per day) (Noedl et al. However, artesunatebased combos are most well-liked within the second and third trimesters (Burger et al. In research in Thailand, the place a excessive fee of resistance to quinine has been documented, pregnant women in the second and third trimesters with uncomplicated malaria were reported to not have critical opposed events or hypoglycemia associated with quinine use (McGready et al. However, quinine-treated patients had a excessive price of recrudescence (33% at day 63) after treatment with supervised quinine for 7 days, compared with solely 2% for mefloquine�artesunate (McGready et al. Parasitologic response was slow and anemia was common within the first four weeks after treatment (McGready et al. For recrudescent infection, quinine (30 mg/kg/day for 7 days) combined with clindamycin (15 mg/kg/day for 7 days) was efficient in a study undertaken on the Burma�Thai border (McGready et al. Current evidence suggests that quinine is inferior to intravenous artesunate for extreme malaria (see Table 177. This trial demonstrated a discount in mortality from 22% within the quinine group to 15% within the artesunate group. However, it should be famous that nearly all of sufferers (86%) on this trial were adults, and the trial was carried out in Southeast Asia, the place malaria transmission is less intense than in Africa. A large randomized trial comparing quinine with artesunate for extreme malaria was carried out in children younger than 15 years in nine African nations (Dondorp et al. Coma and convulsions have been significantly less frequent within the artesunate group, as was post-treatment hypoglycemia. A systematic evaluation of trials evaluating artesunate with quinine in extreme malaria included studies in kids and adults from Asia and Africa (Sinclair et al. This analysis concluded that quinine is less efficacious than intravenous artesunate in preventing dying in extreme malaria and that quinine is associated with a higher incidence of hypoglycemia. In some countries, quinine remains to be utilized in sufferers with extreme malaria owing to inability to entry artesunate. Several small comparative studies have examined the relative efficacy of quinine in opposition to intramuscular artemether in African youngsters (Artemether�Quinine Meta-analysis Study Group, 2001). There was no difference in mortality in African youngsters (in high-transmission areas) compared with Asian children (in lower transmission areas). However, these outcomes may mirror the erratic absorption of intramuscular artemether (Hien et al. A loading dose of quinine in sufferers with severe malaria has been recommended based mostly on pharmacokinetic data (see part four, Mode of drug administration and dosage) (Krishna and White, 1996). A systematic review recognized 4 randomized controlled trials that examined the efficacy of a loading dose of quinine (Lesi and Meremikwu, 2004). This study concluded that there was insufficient evidence to suggest that a loading dose of quinine was related to decrease mortality. However, there was some evidence that a loading dose was related to faster parasite and fever clearance occasions. In one research, the incidence of transient deafness was larger amongst sufferers who acquired a loading dose of quinine, however this was largely reversible (Tombe et al. Rectal quinine may be an alternative route of administration for patients with severe malaria in areas the place intravenous 7. Selected comparative randomized managed trials of quinine (Q) towards artesunate (A) for severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria.
Diseases - SCOT deficiency
- Richieri Costa Da Silva syndrome
- M?bius axonal neuropathy hypogonadism
- Dominant ichthyosis vulgaris
- Devic syndrome
- Buttiens Fryns syndrome
- Fanconi ichthyosis dysmorphism
- Mitochondrial cytopathy (generic term)
- Ruvalcaba Myhre Smith syndrome (BRR)
Benemid 500 mg purchase otcIn complete diagnostic pain treatment center tomball texas benemid 500 mg purchase otc, 41 sufferers in the placebo group developed parasitemia and 2 within the atovaquone� proguanil group developed parasitemia pain management treatment plan template 500mg benemid cheap free shipping. In a double-blind placebo-controlled trial to assess the influence of atovaquone�proguanil on the immunogenicity of cholera and typhoid vaccines in 330 Gabonese children (4�16 years of age) achilles heel pain treatment exercises 500mg benemid order, no significant distinction in adverse occasions including headache, stomach pain, cough, fever, vomiting, or diarrhea was observed between atovaquone� proguanil and placebo (Faucher et al. Treatment of uncomplicated malaria Atovaquone�proguanil is appropriate for therapy of uncomplicated P. Standard treatment for adults consists of one thousand mg/250 mg atovaquone�proguanil for 3 days. Dose changes are required based mostly on weight for kids and for adults with significant renal impairment (see Table 184. There have been a quantity of randomized comparative trials assessing atovaquone�proguanil at commonplace dose for the remedy of uncomplicated malaria (1000 mg of atovaquone and 250 mg of proguanil) (Radloff et al. The curative efficacy (clinical remedy at 28 days) in these trials ranged between 87% and 100% in adults. There have been two comparative trials in pediatric cohorts assessing the efficacy of atovaquone�proguanil in relation to halofantrine and amodiaquine (Anabwani et al. Artesunate has also been used in combination with atovaquone�proguanil in two scientific trials. In the first, a randomized open-label three-arm trial on the northwest border of Thailand of sufferers with uncomplicated P. Polymerase chain reaction�confirmed recrudescence occurred in 13 of the artesunate�mefloquine, three of the artesunate�atovaquone�proguanil, and 15 of the atovaquone�proguanil patients. All regimens have been usually properly tolerated, though the artesunate�atovaquone� proguanil regimen was superior. In the second of those trial, 338 Cameroonian children 5 years or younger have been randomized to artesunate�amodiaquine, atovaquone�proguanil, or 3144 Atovaquone�Proguanil artesunate�atovaquone�proguanil (Tahar et al. Artesunate� atovaquone�proguanil was the superior treatment, with a 95% treatment price. Causal prophylactic efficacy of atovaquone�proguanil (Malarone) in a human problem model. Atovaquone and proguanil versus amodiaquine for the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in African infants and young children. Atovaquone plus proguanil versus halofantrine for the treatment of imported acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in non-immune adults: a randomized comparative trial. Atovaquone� proguanil compared with chloroquine and chloroquine�sulfadoxine� pyrimethamine for therapy of acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Philippines. Atovaquone�proguanil versus chloroquine�proguanil for malaria prophylaxis in nonimmune pediatric travelers: outcomes of an international, randomized, open-label research. Evaluation of atovaquone in the remedy of patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. The causal prophylactic activity of the novel hydroxynaphthoquinone 566C80 in opposition to Plasmodium berghei infections in rats. Evidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria resistant to atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride: case stories. Efficacy of atovaquone/ proguanil for malaria prophylaxis in kids and its effect on the immunogenicity of stay oral typhoid and cholera vaccines. Modified fixed-ratio isobologram technique for studying in vitro interactions between atovaquone and proguanil or dihydroartemisinin against drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Malarone therapy failure and in vitro affirmation of resistance of Plasmodium falciparum isolate from Lagos, Nigeria. Site of action of the antimalarial hydroxynaphthoquinone, 2-[trans-4-(4-chlorophenyl) cyclohexyl]-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (566C80). Confirmation of emergence of mutations related to atovaquone�proguanil resistance in unexposed Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Africa. Population pharmacokinetics of atovaquone in sufferers with acute malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum. The dihydrofolate-thymidylate synthetase gene within the drug resistance of malaria parasites. The effects of antimalarials on the Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. In vitro atovaquone/ proguanil susceptibility and characterisation of the cytochrome b gene of Plasmodium falciparum from different endemic regions of Thailand. Efficacy and security of atovaquone� proguanil in treating imported malaria in Japan: the second report from the analysis group. Efficacy of atovaquone� proguanil for treatment of acute multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Thailand. Emergence of atovaquone�proguanil resistance throughout remedy of Plasmodium falciparum malaria acquired by a non-immune north American traveller to west Africa. Atovaquone/proguanil remedy for Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria in Indonesians who lack clinical immunity. Atovaquone inhibits the glucuronidation and increases the plasma concentrations of zidovudine. First case of emergence of atovaquone resistance in Plasmodium falciparum throughout second-line atovaquone�proguanil treatment in South America. Randomised placebo-controlled study of atovaquone plus proguanil for malaria prophylaxis in youngsters. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of atovaquone/proguanil for the prevention of Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax malaria among migrants to Papua, Indonesia. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride compared with chloroquine or pyrimethamine/sulfodaxine for 7. Clinical makes use of of the drug 3145 treatment of acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Peru. Malarone (atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride): a review of its scientific development for remedy of malaria. Atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride adopted by primaquine for therapy of Plasmodium vivax malaria in Thailand. A randomized comparison of artesunate�atovaquone�proguanil versus quinine in treatment for uncomplicated falciparum malaria during pregnancy. Atovaquone and proguanil versus pyrimethamine/sulfadoxine for the treatment of acute falciparum malaria in Zambia. Apparent absence of atovaquone/ proguanil resistance in 477 Plasmodium falciparum isolates from untreated French travellers. Severe atovaquone-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria in a Canadian traveler returned from the Indian subcontinent. The security of atovaquone/proguanil in long-term malaria prophylaxis of nonimmune adults. Novel mutation in cytochrome B of Plasmodium falciparum in certainly one of two atovaquoneproguanil therapy failures in vacationers getting back from same site in Nigeria. Examination of some components answerable for a food-induced enhance in absorption of atovaquone. Randomized trial of artesunate� amodiaquine, atovaquone�proguanil, and artesunate�atovaquone� proguanil for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in children. Atovaquone�proguanil (malarone): an effective treatment for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in travelers from Denmark. Efficacy and pharmacokinetics of atovaquone and proguanil in youngsters with multidrugresistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. First case of emergence of atovaquone�proguanil resistance in Plasmodium falciparum throughout therapy in a traveler in Comoros. Genetic affirmation of atovaquone� proguanil�resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria acquired by a nonimmune traveler to East Africa. Tolerability of malaria chemoprophylaxis in non-immune travellers to sub-Saharan Africa: multicentre, randomised, double blind, 4 arm research. Efficacy and safety of atovaquone/proguanil as suppressive prophylaxis for Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Malaria prophylaxis for aircrew: safety of atovaquone/proguanil in healthy volunteers beneath plane cabin pressure situations.
Benemid 500 mg order on lineTreatment of extreme malaria within the United States with a steady infusion of quinidine gluconate and trade transfusion pain treatment center of greater washington justin wasserman generic 500mg benemid with mastercard. Chloroquine pain treatment for uti discount 500 mg benemid visa, quinine and quinidine inhibit calcium release from macrophage intracellular shops by blocking inositol 1 pain treatment in acute pancreatitis order benemid 500 mg on-line,4,5-trisphosphate binding to its receptor. Randomized comparability of artesunate and quinine within the therapy of extreme falciparum malaria. Clindamycin plus quinine for treating uncomplicated falciparum malaria: a scientific evaluate and meta-analysis. High incidence of hypoglycaemia in African patients treated with intravenous quinine for severe malaria. In vitro activities of quinine and different antimalarials and pfnhe polymorphisms in Plasmodium isolates from Kenya. Antimalarial drug susceptibility and level mutations associated with drug resistance in 248 Plasmodium falciparum isolates imported from Comoros to Marseille, France in 2004 2006. Controlled trial of 3-day quinine� clindamycin treatment versus 7-day quinine remedy for grownup travelers 7. Clinical makes use of of the drug 3073 with uncomplicated falciparum malaria imported from the tropics. Quinine treatment of severe falciparum malaria in African kids: a randomized comparison of three regimens. Hypoglycaemia and counterregulatory hormone responses in extreme falciparum malaria: remedy with Sandostatin. Quinine pharmacokinetics and toxicity in pregnant and lactating girls with falciparum malaria. Molecular evaluation of pfatp6 and pfmdr1 polymorphisms and their association with in vitro sensitivity in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Thai�Myanmar border. Resistance to antimalarials in Southeast Asia and genetic polymorphisms in pfmdr1. Prevalence of in vitro resistance to eleven normal or new antimalarial medicine among Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Pointe-Noire, Republic of the Congo. Adverse results in patients with acute falciparum malaria treated with artemisinin derivatives. Therapeutic responses to quinine and clindamycin in multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. Adverse impact of rifampin on quinine efficacy in uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Dose-dependent resorption of quinine after intrarectal administration to children with reasonable Plasmodium falciparum malaria. The in-vitro susceptibilities of Ghanaian Plasmodium falciparum to antimalarial drugs. Drug remedy for Plasmodium falciparum malaria resistant to pyrimethamine�sulfadoxine (Fansidar). In vitro exercise of antimalarials in opposition to medical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum in Yaounde, Cameroon. Continuous-infusion quinidine gluconate for treating youngsters with extreme Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Disposition of quinine in plasma, red blood cells and saliva after oral and intravenous administration to healthy grownup Africans. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites conferred by pfcrt mutations. Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid) and plasma protein binding of quinine in falciparum malaria. Polymorphism of Plasmodium falciparum Na+/H+ exchanger is indicative of a low in vitro quinine susceptibility in isolates from Viet Nam. Effects of concurrent administration of nevirapine on the disposition of quinine in wholesome volunteers. Pharmacokinetic interactions between ritonavir and quinine in wholesome volunteers following concurrent administration. Abnormal circulatory control in falciparum malaria: the effects of antimalarial drugs. Studies on the chemotherapy of the human malarias: the physiological disposition and antimalarial activity of the cinchona alkaloids. Drug interplay between cyclosporine A and quinine in a renal transplant affected person with malaria. Ototoxic reactions of quinine in wholesome individuals and sufferers with Plasmodium falciparum infection. Effects on macaque embryos of medication reported or suspected to be teratogenic to humans. Blood glucose levels in Malawian youngsters earlier than and through the administration of intravenous quinine for severe falciparum malaria. Quinine loading dose in extreme Falciparum malaria at Kenyatta National Hospital, Kenya. Blackwater fever in southern Vietnam: a prospective descriptive research of 50 circumstances. Therapeutic efficacy of clindamycin together with quinine for treating uncomplicated malaria in a village dispensary in Gabon. Therapeutic results of chloroquine in combination with quinine in uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Plasma protein binding of quinine: binding to human serum albumin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and plasma from sufferers with malaria. Quinine with tetracycline for the therapy of drug-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Intramuscular loading dose of quinine for falciparum malaria: pharmacokinetics and toxicity. Quinine pharmacokinetics and toxicity in cerebral and uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Towards optimal regimens of parenteral quinine for younger African kids with cerebral malaria: the importance of unbound quinine concentration. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Thailand: in vitro monitoring. Antimalarial drugs: latest advances in molecular determinants of resistance and their clinical significance. Characterization of Plasmodium falciparum isolated from the Amazon area of Brazil: evidence for quinine resistance. Its official chemical name is (R*,S*)-(�)-2-piperidnyl-2,8-bis (trifluromethyl)4-quinolinemethanol hydrochloride (Roche, 2003a). Mefloquine is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 418 (Roche, 2003a). The commercially out there formulation is a racemate of the 11R,2S and 11S,2R enantiomers. The compound belongs to the category of anti-malarials generally referred to as "quinoline methanol. For the Lariam formulation, the inactive components are ammonium�calcium alginate, corn starch, crospovidone, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, poloxamer 331, and talc (Roche, 2003a). Mefloquine is commercially out there as a mefloquine hydrochloride salt within the form of both the unique 250-mg tablet (Lariam; Roche) or a 275-mg generic pill (Mephaquin; Mepha) (Verdun, 2006). In the outline of the drug that follows, the reader must be conscious that a lot of the detailed background information pertains to the unique brand name formulation (Lariam). The two formulations are totally different in some respects, and these differences are outlined the place clinically important. A fixed-dose mixture of mefloquine�artesunate for adults and bigger children is now available in lots of endemic international locations (Nosten and White, 2007). In Southeast Asia, mefloquine was combined with artesunate initially as a outcome of mefloquine monotherapy became ineffective, and now could be used as a software to prevent the emergence of artemisinin-resistant malaria strains. This historic background of mefloquine resistance is reflected by typically decreased susceptibility of medical isolates in laboratory testing and the existence of genetic correlates of resistance.
Benemid 500 mg discount with mastercardRisks in being pregnant and fetal toxicity No human research have been carried out pain gum treatment benemid 500 mg buy discount online, and clinical trials have excluded pregnant and lactating women st john pain treatment center purchase benemid 500 mg otc. Reproductive toxicity checks have been undertaken in rats and rabbits with statistically important will increase in fetal malformation and toxicity only at maternally poisonous doses (10 mg/kg/day; no observed antagonistic impact stage 5 mg/kg/day) heel pain treatment video benemid 500 mg buy cheap line. From these research moxidectin was decided to be neither teratogenic nor a developmental toxicant (Fort Dodge Animal Health, 2005). Outcomes of scientific studies with onchocerciasis-infected individuals have yielded favorable outcomes relative to ivermectin. The discount 3366 Ivermectin and Moxidectin levamisole plus albendazole, and their efficacy towards Onchocerca volvulus. A randomized, single-ascendingdose, ivermectin-controlled, double-blind examine of moxidectin in Onchocerca volvulus infection. Ivermectin distribution within the plasma and tissues of sufferers infected with Onchocerca volvulus. Subcutaneous ivermectin use in the treatment of severe Strongyloides stercoralis infection: two case stories and a dialogue of the literature. Characterisation of macrocyclic lactone resistance in two field-derived isolates of Cooperia oncophora. Effect of single-dose ivermectin on Onchocerca volvulus: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Sustained clearance of Mansonella ozzardi an infection after treatment with ivermectin in the Brazilian Amazon. Macrocyclic lactones: distribution in plasma lipoproteins of a number of animal species including people. Treatment of scabies with oral ivermectin in 15 infants: a retrospective study on tolerance and efficacy. A comparison of the efficacy of single doses of albendazole, ivermectin, and diethylcarbamazine alone or in combinations towards Ascaris and Trichuris spp. Randomized clinical trial on ivermectin versus thiabendazole for the remedy of strongyloidiasis. Analysis of the mdr-1 gene in patients co-infected with Onchocerca volvulus and Loa loa who skilled a post-ivermectin critical opposed event. Macrocyclic lactone resistance in Dirofilaria immitis: failure of heartworm preventives and investigation of genetic markers for resistance. Genetic polymorphism of the B-tubulin gene of Onchocerca volvulus in ivermectin naive patients from Cameroon, and its relationship with fertility of the worms. Efficacy of ivermectin treatment of cutaneous gnathostomiasis evaluated by placebocontrolled trial. Comparative evaluation of systemic drugs for his or her results towards Anopheles gambiae. Resistance to the macrocyclic lactone moxidectin is mediated in part by membrane transporter P-glycoproteins: implications for management of drug resistant parasitic nematodes. Comparative efficacy and safety of topical permethrin, topical iverectin and oral ivermectin in sufferers of uncomplicated scabies. Absence of any adverse effect of inadvertent ivermectin treatment throughout pregnancy. Equivalent therapeutic efficacy and safety of ivermectin and lindane within the remedy of human scabies. A cluster randomized research of the protection of built-in remedy of trachoma and lymphatic filariasis in kids and adults in Sikasso, Mali. The results of body composition on the pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously injected ivermectin and moxidectin in pigs. Cloning of an avermectin delicate glutamate gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. First documentation of in vivo and in vitro ivermectin resistance in Sarcoptes scabiei. Doxycycline results in sterility and enhanced killing of female Onchocerca volvulus worms in an space with persistent microfilaridermia after repeated ivermectin therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Adverse reactions after large-scale treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin: mixed results from eight community trials. Strongyloides disseminated an infection efficiently handled with parenteral ivermectin: case report with drug focus measurements and review of the literature. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the adulticidal efficacy of repeat high-dose ivermectin in bancroftian filariasis. Secondary effects of the remedy of hypermicrofilaremic loiasis utilizing ivermectin. Enhancement of moxidectin bioavailability in lamb by a pure flavonoid: quercetin. The relative systemic availability of ivermectin after administration as capsule, pill, and oral solution. The effect of azithromycin on ivermectin pharmacokinetics-a population pharmacokinetic mannequin evaluation. Ivermectin selection on beta-tubulin: evidence in Onchocerca volvulus and Haemonchus contortus. A comparability of genetic polymorphism in populations of Onchocerca volvulus from untreated and ivermectintreated sufferers. Long-term suppression of Mansonella streptocerca microfilariae after treatment with ivermectin. Reductions of non-pest insects in dung of cattle treated with endectocides: a comparison of four products. The efficacy of ivermectin in the chemotherapy of gastrointestinal helminthiasis in people. Treatment for crusted scabies: limitations and side effects of therapy with Ivermectin. Effects of standard and excessive doses of ivermectin on adult worms of Onchocerca volvulus: a randomised managed trial. Anthelmintic resistance to ivermectin and moxidectin in gastrointestinal nematodes of cattle in Europe. Ivermectin: A evaluation of its antifilarial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and medical efficacy in onchocerciasis. Haemonchus contortus P-glycoprotein-2: in situ localisation and characterisation of macrocyclic lactone transport. Effects of annual mass treatment with ivermectin for onchocerciasis on the prevalence of intestinal helminths. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating excessive doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects. Inadvertent publicity of pregnant ladies to ivermectin and albendazole during mass drug administration for lymphatic filariasis. Rapid and preferential sebum secretion of ivermectin: a model new issue that will determine drug responsiveness in sufferers with scabies. The lack of affect of food and local alcoholic brew on the blood level of Mectizan((R)) (ivermectin). Impact of an ivermectin mass drug administration on scabies prevalence in a distant Australian aboriginal neighborhood. Short- and long-term motion of multiple doses of ivermectin on loiasis microfilaremia. The impact of a highfat breakfast on the pharmacokinetics of moxidectin in healthy male subjects: a randomized part I trial. Relative bioavailability of liquid and pill formulations of the antiparasitic moxidectin. Determination of ivermectin in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. Double-blind study of ivermectin and diethylcarbamazine in African onchocerciasis sufferers with ocular involvement. Community administration of endemic scabies in remote aboriginal communities of northern Australia: low remedy uptake and high ongoing acquisition. Control of scabies, skin sores and haematuria in youngsters in the Solomon Islands: another role for ivermectin. P-glycoproteins and other multidrug resistance transporters within the pharmacology of anthelmintics: prospects for reversing transport-dependent anthelmintic resistance.
Vitamin B-3 (Niacin And Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)). Benemid. - Migraine headache, dizziness, depression, motion sickness, alcohol dependence, improving orgasm, acne, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other conditions.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Prevention of cataracts, an eye condition.
- Reducing the risk of a second heart attack in men with heart or circulatory disorders.
- Diarrhea from an infection called cholera.
- Heart disease, including hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Treatment and prevention of niacin deficiency, and certain conditions related to niacin deficiency such as pellagra.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Diabetes, types 1 and 2.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96888
Benemid 500mg safePersistent neutropenic fever A massive pain medication for dogs natural purchase benemid 500mg without a prescription, randomized trial of 837 neutropenic patients compared voriconazole with liposomal amphotericin B for empirical treatment of invasive fungal an infection (Walsh et al foot pain treatment video discount benemid 500 mg line. Eligible sufferers included those who had obtained chemotherapy for leukemia chronic pain treatment guidelines benemid 500mg discount fast delivery, lymphoma, or other cancer or who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Patients had received at least ninety six hours of systemic antibiotics and were febrile to 38�C. However, fewer breakthrough invasive fungal infections have been documented in the voriconazole group (voriconazole 2%, liposomal amphotericin B 5%) and voriconazole 7f. Of the nine remaining patients, eight sufferers received benefit from voriconazole, together with five sufferers who responded fully to remedy. This relatively highresponse rate means that voriconazole could have a task within the remedy of refractory Penicillium infections, though itraconazole also appears effective (see Chapter 154, Itraconazole). Cryptococcosis the potential position of voriconazole in the therapy of refractory cryptococcosis proven in an open-label, salvage trial (Perfect et al. Of the 18 sufferers in this trial with refractory cryptococcosis, 39% responded to voriconazole treatment. Voriconazole had good efficacy (> 80% with improvement) in case reports of use for endemic fungi including histoplasmosis, blastomycosis, and coccidioidomycosis (Freifeld et al. A retrospective review of 21 sufferers with coccidioidomycosis refractory to fluconazole or liposomal amphotericin B discovered a 67% improvement price after 6 months (Kim et al. Of nine children who failed a minimal of 6 weeks of major remedy, eight responded to an induction routine of caspofungin plus voriconazole, followed by upkeep with oral voriconazole (Levy et al. The authors concluded that their most popular routine included voriconazole somewhat than fluconazole or itraconazole. Complete or partial response was observed in 87% of sufferers receiving voriconazole 200 mg twice a day and 94% of these treated with itraconazole a hundred mg twice a day (Telles et al. However, a more modern rat study suggested that the efficacy of voriconazole for this infection was inferior to that of itraconazole or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, that are the usual brokers for mild to reasonably extreme infections (Granzoto et al. Analysis of voriconazole concentrations in 9 sufferers on upkeep voriconazole therapy for disseminated histoplasmosis (after induction of remission with amphotericin B or itraconazole) revealed the everyday wide selection, though no patient relapsed (Freifeld et al. It was also the least active of all of the azoles, amphotericin B, and terbinafine towards S. These outcomes had been confirmed in vivo in a murine mannequin of disseminated an infection with these organisms-there was modest effect against S. Amphotericin B and/or itraconazole, and probably posaconazole or terbinafine, are higher alternatives in opposition to these organisms, though surgical debridement can be essential (Aung et al. Fungal keratitis A comparative study of voriconazole 1% versus natamycin 5% for remedy of fungal keratitis showed higher longer term 7. Prospective open-label study of the administration of two-percent voriconazole eye drops. In vitro pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic modeling of voriconazole exercise towards Aspergillus species in a model new in vitro dynamic mannequin. A randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, multicenter trial of voriconazole and fluconazole within the remedy of esophageal candidiasis in immunocompromised sufferers. Hepatic security of voriconazole after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In vivo pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a new triazole, voriconazole, in a murine candidiasis mannequin. Scedosporium apiospermum endopthalmitis handled early with intravitreous voriconazole leads to restoration of vision. Susceptibility of Sporothrix brasiliensis isolates to amphotericin B, azoles, and terbinafine. Systematic evaluation and mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis of randomized medical trials of main oral antifungal prophylaxis in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Utilization of omeprazole to augment subtherapeutic voriconazole concentrations for treatment of Aspergillus infections. Pharmacokinetics and security of 14 days intravenous voriconazole in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Rapid induction of multiple resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus fumigatus during azole remedy: a case research and review of the literature. Intrapulmonary penetration of voriconazole in sufferers receiving an oral prophylactic routine. Compassionate use of voriconazole in newborn infants diagnosed with extreme invasive fungal sepsis. Clinical follow tips for the administration of blastomycosis: 2008 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Effect of proton pump inhibitor on plasma voriconazole focus in Thai sufferers. Exploring azole antifungal drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus with special reference to resistance mechanisms. Chronic phototoxicity and aggressive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in kids and adults throughout therapy with voriconazole. Voriconazole serum concentrations in overweight and overweight immunocompromised patients: a retrospective evaluation. Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the therapy of acute invasive aspergillosis. Therapeutic monitoring of voriconazole in children less than 3 years of age: a case report and summary of voriconazole concentrations for 10 youngsters. Voriconazole pharmacokinetics and exposure�response relationships: assessing the hyperlinks between publicity, efficacy and toxicity. Understanding variability with voriconazole utilizing a population pharmacokinetic method: implications for optimal dosing. Voriconazole pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring: a multi-center research. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic penalties and medical relevance of cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and security of voriconazole intravenous-to-oral switch in immunocompromised children and wholesome adults. Adverse results of voriconazole: analysis of the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole in the management of invasive fungal infections: a critical evaluate. A multistep voriconazolerelated phototoxic pathway may lead to pores and skin carcinoma: outcomes from a French nationwide examine. Modest efficacy of voriconazole in opposition to murine infections by Sporothrix schenckiiand lack of efficacy against Sporothrix brasiliensis. Intravitreal voriconazole as major remedy for endogenous Aspergillus endophthalmitis. Determination of plasma unbound fraction of voriconazole in sufferers treated with a prophylactic or a curative remedy. Relationship of blood level and susceptibility in voriconazole therapy of histoplasmosis. Integrated population pharmacokinetic evaluation of voriconazole in kids, adolescents, and adults. Fungal endophthalmitis efficiently treated with intravitreal voriconazole injection. Reversible skeletal illness and high fluoride serum ranges in hematologic sufferers receiving voriconazole. In vitro activities of new and established triazoles towards opportunistic filamentous and dimorphic fungi. Pharmacokinetics of sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin and voriconazole in patients with end-stage renal failure throughout remedy with two hemodialysis systems and hemodiafiltration. Determination of vitreous, aqueous, and plasma focus of orally administered voriconazole in humans. Relationship between trough plasma and epithelial lining fluid concentrations of voriconazole in lung transplant recipients. Quantification of brain voriconazole ranges in wholesome adults using fluorine magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Software for dosage individualization of voriconazole for immunocompromised patients. Frequency and evolution of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus related to treatment failure.
500mg benemid purchase with visaSubjects have been enrolled from 15 completely different travel clinics in the Netherlands pain management utilization cheap benemid 500 mg with mastercard, Germany pain treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome benemid 500 mg without prescription, the United Kingdom pain treatment goals benemid 500mg purchase visa, Canada, and South Africa. Subjects who traveled to malaria-endemic areas for as a lot as 28 days underwent follow-up at days 7, 28, and 60 after their return for evaluation of malaria exposure and antagonistic drug effects. Treatment with atovaquone�proguanil was higher tolerated than treatment with mefloquine, with much less headache (19% vs. Efficacy was evaluated as a secondary finish point, but there were no confirmed instances of malaria in both arm of this research. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial examine of atovaquone�proguanil versus placebo was carried out in 297 individuals who migrated from areas of nonendemicity in Indonesia to Papua (high malaria endemicity) 26 months before commencement of the study (Ling et al. Volunteers were aged 12�65 years and were treated with radical healing remedy (atovaquone�proguanil 1000/250 mg every day three days followed by 30-mg tablets containing primaquine base, day by day for 14 days earlier than graduation of the prophylactic section. In a randomized placebo-controlled trial of atovaquone� proguanil as chemoprophylaxis for as a lot as 20 weeks in 295 sufferers in Papua, Indonesia, solely 3 developed P. These trials have demonstrated a protective efficacy of 95�100% in semi-immune people (Shanks et al. A double-blind placebo-controlled trial to assess efficacy, safety, and tolerability of atovaquone�proguanil in western Kenya, an space with endemic malaria, confirmed 100% efficacy of atovaquone�proguanil (Shanks et al. Assessment was conducted in 198 adults in certainly one of three teams who received (1) atovaquone�proguanil at 250/100 mg/daily (n = 68), (2) atovaquone�proguanil 500/200 mg/daily (n = 65), or (3) placebo (n = 65) for 10 weeks. The treatment was nicely tolerated, with commonly reported opposed reactions at normal dose of dyspepsia (4%), gastritis (6%), and stomach pain (5%), although there was no important distinction with placebo. The efficacy end point was the proportion of topics who developed parasitemia in the course of the prophylaxis period. Parasitemia developed in 52% of those taking placebo and not one of the subjects taking atovaquone�proguanil, correlating with a 100 percent efficacy for the prevention of malaria on this cohort. A randomized placebo-controlled trial to assess the protection and efficacy of atovaquone�proguanil for malaria prophylaxis was undertaken in of 320 youngsters (4�16 years of age) living in Gabon (Lell et al. After a healing course of three days of atovaquone�proguanil, a hundred twenty five received a weightadjusted prophylactic dose of atovaquone�proguanil and one hundred forty received placebo for 12 weeks. There were three withdrawals (2 had been misplaced to follow-up and 1 withdrew consent) within the placebo group and 10 (7 lost to follow-up and 3 protocol violations) in the atovaquone�proguanil group. There had been no circumstances of malaria in the atovaquone�proguanil group and 25 instances within the placebo group during the chemosuppressive part. Children within the atovaquone�proguanil group had comparable frequencies of belly pain (33%), headache (14%), vomiting (7%), and nausea (2%) as the placebo group. In complete, 274 have been randomized to atovaquone� proguanil (n = 136) or placebo (n = 138). Thirty of these patients were lost to follow-up (16 atovaquone�proguanil and 14 placebo), 22 had protocol violations (14 atovaquone� proguanil and eight placebo), and 9 withdrew consent (4 atovaquone�proguanil and 5 placebo). Commonly reported adverse events have been headache (4%), abdominal pain (3%), and diarrhea (1%), although the rates of those antagonistic reactions have been greater in the placebo group. A randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled field trial to determine the efficacy and safety of Malarone (atovaquone/proguanil) for the prophylaxis of malaria in Zambia. Time-dependent pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism of atovaquone plus proguanil (Malarone) when taken as chemoprophylaxis. The effect of atovaquone on etoposide pharmacokinetics in kids with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Safety and efficacy of atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride for the prophylaxis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in South Africa. Early treatment failure throughout remedy of Plasmodium falciparum malaria with atovaquone� proguanil in the Republic of Ivory Coast. It differs from neomycin by having a hydroxyl group instead of the amino group at position 6. Like other aminoglycosides, it acts by ribosomal binding and inhibition of protein synthesis. Alternative names for paromomycin have been used historically, together with the generic names aminosidine, catenulin, crestomycin, estomycin, hydroximycin, monomycin A, neomycin E, and paucimycin. It is marketed under the commerce names Gabbromicina, Gabromicina, and Gabromycin for parenteral products; Gabbroral, Gabromycin, Kapseal, Humatin, and Pargonyl for oral products; and Leshcutan for the topical product. Paromomycin sulfate consists of a mix of sulfate salts produced by the expansion of strains of Streptomyces rimosus var. As the quantities of sulfate ultimately product differ by up to 10% or extra, the label of paromomycin injection currently marketed expresses efficiency by method of paromomycin base; 15 mg of paromomycin sulfate per kilogram is equivalent to 11 mg of paromomycin base per kilogram. It is heat-stable up to 120�C for as much as 24 hours however loses exercise at temperatures over 130�C. Routine susceptibility the spectrum of activity of paromomycin encompasses most Gram-negative and plenty of Gram-positive bacteria, some protozoa, and a few cestodes (Coffey et al. It is notable as the most potent antiprotozoal among the aminoglycosides, and the only one with clinically essential exercise towards Leishmania. In addition, it has activity towards Mycobacterium tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria (Kanyok et al. Oral paromomycin has therapeutic efficacy in opposition to Giardia lamblia (Gardner and Hill, 2001), Entamoeba histo lytica (Stauffer and Ravdin, 2003), and Cryptosporidium par vum (Abubakar et al. However, its early bactericidal exercise in patients with tuberculosis was weak, much like that of 3149 3150 Paromomycin streptomycin (Donald et al. Various in vitro research have shown that paromomycin is lively in opposition to both the extracellular promastigote and intracellular amastigote forms of the Leishmania parasite (Neal and Croft, 1984; Gebre-Hiwot et al. Nevertheless, experimental data obtained with mouse fashions and naturally contaminated canines (the zoonotic reservoir for the parasite) demonstrated that paromomycin is efficient in opposition to L. Although all species of Leishmania are prone in vitro to paromomycin and resistance in the medical setting has not but been demonstrated, strains of L. The activity of paromomycin differs between amastigotes and promastigotes, with amastigotes being extra prone (Kulshrestha et al. This has implications for susceptibility testing, because in humans only the amastigote stage is uncovered to drug pressure, however susceptibility testing is commonly carried out on promastigotes. In vitro resistance was extra easily induced in amastigotes than promastigotes, being seen after solely two choice cycles. When solely paromomycin was used to select for resistance, the resulting resistance was secure in the absence of continuing drug strain, and the resistant parasites were still infective to macrophages in vitro and to golden hamsters in vivo (Hendrickx et al. However, when paromomycin was used in combination with other anti-leishmanial agents, the induced resistance was unstable (Garc�a-Hern�ndez et al. There is evidence that clinically essential secondary resistance of Leishmania can occur. If resistance mutations are stable, transmission from such patients would result in main resistance in others. It has been proposed that the distribution of paromomycin and other medicine for leishmaniasis must be restricted to the public sector, where their use could be controlled (Sundar and Murray, 2005). In vitro and in vivo synergy and antagonism A variety of in vitro studies have demonstrated synergy when paromomycin is combined with other anti-leishmanial drugs, specifically antimonials. Synergy has been confirmed in scientific trials, with the combination of paromomycin and sodium stibogluconate being simpler than monotherapy with either drug (Chunge et al. A synergistic effect was similarly seen in vitro when paromomycin was used in two-drug combinations with miltefosine and amphotericin B against Leishmania amazonensis; with meglumine antimoniate and amphotericin B in opposition to Leishmania braziliensis; and with miltefosine, amphotericin B, and azithromycin in opposition to Leishmania infan tum chagasi (de Morais-Teixeira et al. Synergy allowed the use of low-dose paromomycin when combined with low-dose oral miltefosine or parenteral meglumine antimoniate in an in vivo hamster model of L. Use of lower doses of systemic anti-leishmanials also reduces the risk of toxicity, which is common with anti-leishmanial antimonials. The ordinary oral dose of paromomycin for intestinal amebiasis and giardiasis is 25�35 mg/kg every day (administered in three doses with meals for 5�10 days) for adults and kids. As adjunctive therapy in adults with hepatic coma to cut back intestinal bacterial progress, the dose is 4 g day by day in divided doses for 5�6 days. Taenia solium, Taenia saginata, Hymenolepis nana, and Diphyllobothrium latum), it has been superseded by more effective anthelmintics. The dosage regimens used in the small number of studies that have been undertaken have varied (see section 7, Intestinal cestode infections). This binding induces a conformational change, following which ribosomal discrimination is disabled and protein synthesis impaired. The binding site is very conserved, thus explaining its broad antibacterial spectrum. Because paromomycin is cationic, it associates easily with the anionic parts of the bacterial cell wall, facilitating its uptake.

500mg benemid buy with amexStudies using radiolabeled 1% ciclopirox olamine cream revealed penetration into stratum corneum of 0 pain treatment pregnancy cheap benemid 500mg on-line. Penetration by way of the fingernail has additionally been doc umented by the demonstration of antifungal activity against T st john pain treatment center benemid 500mg discount without prescription. The lacquer formulation delivery system of ciclopirox offers a high focus gradient for the transfer of the antifungal agent through the nail plate pain treatment center in morehead ky 500mg benemid purchase visa. After evaporation of risky solvents within the lacquer, the concentration of ciclopirox in the remaining lacquer movie reaches approximately 35%, providing a high focus gradient for penetration into the nail. Radiolabel data reveal penetration into contaminated nails after just one software of the lacquer for mulation. With repeated functions, the antifungal agent is homogeneously distributed via all layers of the toenail, attaining inhibitory and fungicidal concentrations for most pathogens. Although ciclopirox readily penetrates nails, very low levels of ciclopirox are recoverable systemically, even after chronic use (Bohn and Kraemer, 2000). Superficial dermatomycosis Ciclopirox is indicated in the treatment of tinea infections. In another study, ciclopirox was discovered to be efficient in the therapy of tinea pedis related to onychomyco sis (Wu et al. Tinea pedis was cured in 45% and improved in an additional 45% of patients (Wu et al. Onychomycosis Ciclopirox 8% nail lacquer applied once every day for 48 weeks over contaminated nails was safe and efficient within the therapy of distal subungual onychomycosis in sufferers with sort 2 dia betes mellitus receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic remedy (Seebacher et al. The outcomes sup porting the usage of ciclopirox 8% nail lacquer within the remedy of onychomycosis of the toenail without lunula involvement have been obtained from two doubleblind, placebocontrolled research performed in the United States (Gupta et al. In these studies, sufferers with onychomycosis of the good toe nails with out lunula involvement had been treated with ciclopirox 8% topical resolution in conjunction with month-to-month removing of the unattached, contaminated toenail. Complete cure, defined as clear nail and adverse mycology culture, was achieved in 5. The mixture of oral terbinafine and ciclopirox nail lacquer was discovered to be secure and simpler in the treatment of onychomycosis than terbinafine alone, especially in youthful sufferers. In a study evaluating the efficacy of combination therapy with ciclopirox nail lacquer 5c. Clinically essential pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic options There are few knowledge obtainable correlating clinical exercise with the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of ciclopirox. Excretion Renal excretion of ciclopirox olamine as metabolites is the first route of elimination. Drug interactions In contrast to the azoles, glucuronidation is the principle meta bolic pathway of ciclopirox; therefore interactions with medication metabolized by way of the cytochrome P450 system are unlikely. In addition, the applying of ciclopirox olamine 1% lotion plus cream to nails contaminated with T. Evaluation of a model new antifungal cream, ciclopirox olamine 1% in the remedy of cutaneous candidosis. Treatment of tinea versicolor with a new antifungal agent, ciclopirox olamine cream 1%. Combination of oral terbinafine and topical ciclopirox in comparison with oral terbinafine for the therapy of onychomycosis. Dermatopharmacology of ciclopirox nail lacquer topical solution 8% within the remedy of onychomycosis. Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of ciclopirox on the adherence of Candida albicans to human buccal and vaginal epithelial cells. Ciclopirox 8% nail lacquer topical solution for the therapy of onychomycosis in sufferers with diabetes: a multicenter, open-label study. Toward repurposing ciclopirox as an antibiotic towards drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharmacokinetics of ciclopirox olamine after vaginal application to rabbits and patients. The role of topical antifungal remedy for onychomycosis and the emergence of newer agents. Randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blind examine on clinical efficacy of ciclopiroxolamine 1% cream in facial seborrhoeic dermatitis. A multicenter, open-label study to assess the protection and efficacy of ciclopirox topical suspension zero. The impact of ciclopiroxolamine investigated by the use of the freeze-fracture method. Potential of ergosterol synthesis inhibitors to cause resistance or cross-resistance in Trichophyton rubrum. Cutaneous candidiasis Ciclopirox olamine 1% cream is also used within the treatment of cutaneous candidiasis and diaper dermatitis due to C. In two small, uncontrolled research of cutaneous candidiasis, the scientific remedy price reached solely 30%, though nearly all of sufferers experienced some improvement in clinical indicators and symp toms (Jue et al. Tinea (pityriasis) versicolor Clinical and mycologic remedy was achieved in 49% of sufferers handled with ciclopirox olamine 1% cream for 14 days (Anon, 1985b). Ciclopirox olamine 1% cream applied twice daily for 14 days was superior to clotrimazole 1% cream in the deal with ment of tinea versicolor. Clinical and mycologic decision occurred in 77�88% of patients with tinea versicolor treated with ciclopirox olamine 1% cream, compared with 45% treated with clotrimazole 1% cream (Anon, 1985b; Jue et al. Seborrheic dermatitis the antiinflammatory activity of ciclopirox (see above underneath three, Mechanism of drug action) and its potent in vitro activity in opposition to Malassezia spp. In a doubleblind, randomized controlled trial, ciclo pirox olamine shampoo 1% utilized twice weekly for 4 weeks was effective in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in 26% of treated patients compared with 12% of the vehicletreated group (Lebwohl and Plott, 2004). Treated subjects achieved over 75% improvement in contrast with vehicle at days 22 and 29 of therapy. In addition, ciclopirox administered as cream 1% twice day by day for four weeks demon strated a good therapeutic response in mildtomoderate facial seborrheic dermatitis in 63% of sufferers receiving ciclopirox compared with 34% of those receiving automobile (Dupuy et al. Rana Traboulsi and Mahmoud Ghan noum, of the Center for Medical Mycology, Department of seven. Ciclopirox nail lacquer topical solution 8% in the therapy of toenail onychomycosis. In vitro susceptibility testing of ciclopirox, terbinafine, ketoconazole and itraconazole in opposition to dermatophytes and nondermatophytes, and in vitro analysis of mixture antifungal exercise. Interdigital tinea pedis (dermatophytosis simplex and complex) and remedy with ciclopirox 0. Evaluation of fungicidal motion in vitro and in a pores and skin mannequin considering the affect of penetration kinetics of varied commonplace antimycotics. Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation of the antimycotic drug ciclopiroxolamine in animals and man after topical and systemic administration. Results of German multicenter study of antimicrobial susceptibilities of Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes strains causing tinea unguium. Comparison of ciclopirox olamine 1% cream with ciclopirox 1%-hydrocortisone acetate 1% cream within the treatment of infected superficial mycoses. Mode of action of 6-cyclohexyl-1-hydroxy-4-methyl-2(1 H)-pyridone ethanolamine salt (Hoe 296). A multicenter, open-label examine of the efficacy and safety of ciclopirox nail lacquer solution 8% for the treatment of onychomycosis in sufferers with diabetes. Sporocidal impact of amorolfine and other antimycotics used in the remedy of fungal nail infections. The safety and efficacy of ciclopirox olamine for the remedy of seborrheic dermatitis. It is the second antifungal agent of the hydroxypyridone antifungals, together with ciclopirox (see Chapter 164, Ciclopirox). In distinction with ciclopirox olamine, rilopirox reveals robust activity in opposition to yeast, especially Candida albicans (Raether and Hanel, 1990). However, later studies counsel a task for this drug in the remedy of tinea versicolor, seborrheic dermatitis, and oropharyngeal candidiasis (Nenoff et al. All strains with lowered fluconazole susceptibility were vulnerable to rilopirox, including C. Rilopirox has demonstrated potent in vitro exercise against Malassezia furfur, which suggests a medical utility in the therapy of tinea versicolor and seborrheic dermatitis (Nenoff and Haustein, 1997). In addition, in vitro research confirmed that subinhibitory concentrations of rilopirox impair the adhesion process of Candida to each buccal and vaginal cells (Braga et al. Rilopirox has been shown to inhibit the expansion of 38 fluconazole-susceptible and -resistant strains of Candida species, including C. Rilopirox acts by damaging the cell membrane of the fungus and impairing a number of metabolic enzyme systems by way of its robust chelating motion, thus inhibiting iron-dependent enzymes.

500mg benemid purchase amexNotably pain treatment wellness center purchase benemid 500mg on-line, a therapeutic drug monitoring reference laboratory discovered that 70% of 202 serum samples from sufferers receiving the oral suspension formulation contained less than seven-hundred ng/ml of posaconazole (Thompson et al advanced diagnostic pain treatment center new haven benemid 500mg cheap online. These knowledge counsel that therapeutic drug monitoring ought to be performed when administering the oral suspension formulation heel pain treatment stretches benemid 500mg discount mastercard. Because the delayed-release tablet and the intravenous formulation are extra dependable in archiving the goal common steady-state concentrations, therapeutic drug monitoring many not be needed for those formulations. Excretion Posaconazole undergoes minimal metabolism (15%) and is primarily excreted unchanged into the feces (Krieter et al. In healthy volunteers receiving a single 400-mg dose of [14C] posaconazole, 14% of radioactivity was recovered in the urine (Krieter et al. Examination of posaconazole metabolites in healthy volunteers demonstrates that virtually all of metabolites characterize glucuronide conjugates somewhat than oxidative metabolic merchandise (Krieter et al. Hence it has the capacity for drug interactions by way of these mechanisms (see Table 157. Dosages of those immunosuppressants ought to be lowered and drug ranges must be fastidiously monitored. In a small research of six sufferers receiving posaconazole, cyclosporine publicity increased and required cyclosporine dosage reduction of 14�29% in four sufferers (Sansone-Parsons et al. Like other triazoles, co-administration with drug inducers can lower posaconazole serum ranges. Posaconazole also has the potential for drug interactions by interference of P-glycoprotein drug transporters. In vitro research counsel that posaconazole, though weak compared to ketoconazole and itraconazole, is a substrate and inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (Merck Sharp & Dohme, 2009; Sansone-Parsons et al. The role of P-glycoprotein in posaconazole pharmacokinetics and drug interactions ought to be additional investigated. Gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting) have been reported in 15% of sufferers receiving posaconazole for persistent febrile neutropenia or refractory invasive fungal infection (Ullmann et al. Therefore, monitoring of liver function exams is recommended before and during remedy. Hence, in patients with moderate to extreme renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance (CrCl) < 50 ml/min) posaconazole oral formulations, as a substitute of the intravenous formulation, ought to be used- except the profit outweights the chance. In very young canine (dosed from 2�8 weeks of age), receiving the intravenous formulation, an elevated incidence of brain ventricle enlargement was observed. Juvenile canine (4 days to 9 months of age) receiving an oral formulation of posaconazole showed no neurologic, behavioral or developmental abnormalities (Merck Sharp & Dohme, 2009). A randomized trial comparing posaconazole suspension to commonplace azole prophylaxis (fluconazole or itraconazole) in 602 neutropenic patients present process chemotherapy for 2852 Posaconazole acute myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome discovered fewer invasive fungal infections in sufferers receiving posaconazole (2%) than in those receiving either fluconazole or itraconazole (8%) (Cornely et al. Invasive aspergillosis was identified in fewer sufferers receiving posaconazole (1%) than commonplace azole prophylaxis (7%). The fee of invasive candidiasis was similar between the arms (posaconazole 1%, fluconazole or itraconazole < 1%). Notably, Kaplan�Meier evaluation recognized a big survival benefit for sufferers receiving posaconazole. The estimated variety of patients on this cohort wanted to treat to stop one invasive fungal an infection was 16. Analysis of the first endpoint, incidence of invasive fungal an infection (posaconazole 5. Although the superiority of posaconazole was not confirmed, posaconazole was significantly more successful in preventing invasive aspergillosis (posaconazole 2. Two hundred and ten patients received 300 mg posaconazole (as tablets) once day by day. The desk formulation was properly tolerated by sufferers in danger for invasive fungal illness and demonstrated a safety profile much like that reported for the suspension formulation. Overall, 97% of all patients achieved the goal day by day exposure of 500 and 2500 ng/ml (Cornely et al. In two separate cost-effectiveness research, posaconazole was thought-about very more doubtless to be a cheap different to fluconazole or itraconazole in the prevention of invasive fungal infections among neutropenic sufferers (de la Camara et al. Another single-center compassionate use trial enrolled fifty three sufferers with hematologic malignancies who had been refractory or intolerant (renal failure, organ dysfunction) to a minimal of 7 days of conventional remedy for invasive aspergillosis (Raad et al. Patients receiving posaconazole salvage remedy (800 mg every day, divided doses) had been in contrast with 52 sufferers receiving high-dose lipid formulation of amphotericin B (7. The clinical response fee was greater in sufferers receiving posaconazole (40%) than in these receiving either high-dose liposomal amphotericin B (8%) or mixture therapy (11%). Mortality attributed to invasive aspergillosis was considerably decrease in posaconazole-treated patients (39%) in contrast with the control teams (65�68%; p < zero. However, posaconazole has not been immediately in contrast with other agents as main therapy for aspergillosis. Fusariosis In a retrospective evaluation of three open-label trials, 21 sufferers refractory or illiberal to typical therapy (amphotericin B formulation alone or together therapy) were enrolled to obtain posaconazole as salvage remedy (see Table 157. Most patients had hematologic malignancies or acquired hematopoietic stem cell transplantations. Successful consequence (complete or partial response) occurred in 10 (48%) of all 21 patients. Poor end result was seen in sufferers with persistent neutropenia, with solely certainly one of five sufferers (20%) responding to therapy. Altogether, clinical response to posaconazole was similar to that previously reported for salvage remedy with amphotericin B lipid advanced (46%, 12 of 26 patients) and voriconazole (45%, 5 of eleven patients). However, criteria for profitable clinical response were less stringent within the voriconazole examine, incorporating secure illness into the worldwide response outcome. Mucormycosis (formerly termed Zygomycosis) Two European tips on the therapy of mucormycosis suggest posaconazole (oral suspension 200 mg qid) as second-line/salvage therapy of mucormycosis (Cornely et al. The usage of posaconazole in sufferers with mucormycosis refractory or illiberal to standard remedy was examined in two open-label, nonrandomized trials (Table 157. One trial enrolled 24 sufferers with a extensive range of underlying risk elements, together with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, solid organ transplantation, hematologic malignancy, and diabetes mellitus (Greenberg et al. Successful treatment (complete cure and partial response) occurred in 79% of 19 subjects with mucormycosis refractory to and 80% in 5 topics with intolerance to commonplace 7. In this cohort, success of therapy was also linked to surgical debridement of affected tissue. Notably, Mucor circinelloides has lately been described as resistant to posaconazole, suggesting that susceptibility testing could also be helpful in guiding therapy with posaconazole (Khan et al. A retrospective summary of ninety one cases of mucormycosis, in sufferers refractory or intolerant to commonplace therapy (primarily liposomal amphotericin B), investigated the impression of posaconazole salvage therapy (van Burik et al. After 12 weeks, 60% of patients skilled partial or full response and 21% had steady illness. Although numbers were small, 73% of patients with mucormycosis of the brain responded to therapy. After a median follow-up of three months, clinical improvement was noticed in 18 sufferers (56%). Oral posaconazole administration was continued in all 18 responders (mean duration, seventy four days; vary, 10�175 days) without any relapse of invasive mucormycosis. Antifungal remedy of mucormycosis ought to include a lipid formulation of amphotericin B; however, when toxicity happens or stable fungal disease is achieved, therapy may be switched to oral posaconazole 200 mg qid. If impaired renal function is overt or anticipated, major treatment of mucormycosis with posaconazole may be an possibility (Cornely et al. The combination of liposomal amphotericin B and posaconazole for the remedy of invasive mucormycossis is "supported with reasonable strength" (Cornely et al. After one month of therapy, the situations of 11 of 15 sufferers (73%) have been deemed to have improved. In a retrospective evaluation of sufferers prescribed voriconazole (n = 21) or posaconazole (n = 16) for coccidioidomycosis, outcomes have been assessed with each a retrospectively utilized Mycosis Study Group rating and the documented impressions of treating medical practitioners (Kim et al. After a median duration of 6 months of voriconazole and 17 months of posaconazole remedy, 14 of 21 patients (67%) and 12 of sixteen patients (75%), respectively showed improvement in the overall status. Studies of posaconazole in animal fashions of blastomycosis and histoplasmosis have also demonstrated efficacy (Connolly et al.
Purchase benemid 500mg without prescriptionAn open pain treatment center of the bluegrass order benemid 500mg with amex, randomized pain treatment center in morehead ky 500 mg benemid quality, comparative research of oral fluconazole wnc pain treatment center arden nc discount 500 mg benemid mastercard, itraconazole and terbinafine remedy in onychomycosis. Itraconazole in persistent cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis: a randomised controlled trial and systematic review of literature. Fluconazole versus itraconazole for Candida esophagitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Food interaction and steadystate pharmacokinetics of itraconazole capsules in wholesome male volunteers. Enhanced bioavailability of itraconazole in hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin answer versus capsules in wholesome volunteers. Itraconazole for experimental pulmonary aspergillosis: comparison with amphotericin B, interaction with cyclosporin A, and correlation between therapeutic response and itraconazole concentrations in plasma. Itraconazole-related elevated vincristine neurotoxicity: case report and evaluate of literature. Antifungal prophylaxis with itraconazole in prolonged neutropenia: correlation with plasma levels. For cutaneous and lymphocutaneous disease, an initial dose of 200 mg day by day is suggested for 2�4 weeks following lesions decision, usually for a total of 3�6 months. For sufferers with osteoarticular sporotrichosis, the upper itraconazole dosage (200 mg bid) is really helpful for a minimum of 12 months. Amphotercin B ought to be administered as initial remedy in patients with meningeal sporotrichosis, disseminated sporotrichosis, or severe, life-threatening illness. Itraconazole may then be administered as step-down therapy at a dosage of 200 mg bid for no much less than 12 months. In an open-label study of 27 sufferers with culture-positive cutaneous or systemic sprorothricosis, therapy with itraconazole (100�600 mg daily) for 3�18 months yielded an 80% general scientific response rate (Sharkey-Mathis et al. Response charges were similar amongst sufferers with lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis (100%), pulmonary sporotrichosis (75%), articular/osseus sporotrichosis (77%), and multifocal systemic sporotrichosis (66%). In extra research, itraconazole (100 mg daily) demonstrated efficacy for the remedy of lymphocutaneous and fixed form sporotrichosis with scientific response rates of (90�100%) in patients receiving therapy for three to four months (Restrepo et al. In the most important examine of over 600 sufferers, itraconazole remedy yielded a high success price (95%) with a median therapy time of 12 weeks (de Lima Barros et al. Pharmacokinetics and security of a 7-day administration of intravenous itraconazole followed by a 14-day administration of itraconazole oral resolution in patients with hematologic malignancy. A scientific trial of itraconazole within the treatment of deep mycoses and leishmaniasis. Double-blind comparability of itraconazole with griseofulvin in the therapy of tinea corporis and tinea cruris. Terbinafine versus itraconazole: a managed medical comparison in onychomycosis of the toenails. Randomised double blind comparison of terbinafine and itraconazole for remedy of toenail tinea an infection. A double-blind, randomized, stratified controlled research of the treatment of tinea imbricata with oral terbinafine or itraconazole. Itraconazole solution: larger serum drug concentrations and higher scientific response rates than the capsule formulation in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome sufferers with candidosis. Mutations in the cyp51A gene and susceptibility to itraconazole in Aspergillus fumigatus serially isolated from a patient with lung aspergilloma. Treatment of cryptococcal meningitis with mixture itraconazole and flucytosine. Surveillance of triazole susceptibility of colonizing yeasts in patients with haematological malignancies. Intrapulmonary pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of itraconazole and 14-hydroxyitraconazole at regular state. Syncope and cardiac arrhythmia because of an interaction between itraconazole and terfenadine. Twelve weeks of steady oral remedy for toenail onychomycosis brought on by dermatophytes: a double-blind comparative trial of terbinafine 250 mg/day versus itraconazole 200 mg/day. The treatment of aspergillosis and aspergilloma with itraconazole, clinical outcomes of an open worldwide study (1982�1987). Management of fungal pores and skin infections with 15 days itraconazole therapy: a worldwide evaluate. A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic investigation of month-to-month cycles of 1-week pulse therapy with itraconazole. Pulse remedy with one-week itraconazole month-to-month for three or 4 months within the treatment of onychomycosis. Randomized double-blind comparison of short-term itraconazole and terbinafine therapy for toenail onychomycosis. Itraconazole within the treatment of dermatophytoses: a comparability of two day by day dosages. Two-week oral treatment of tinea pedis, evaluating terbinafine (250 mg/day) with itraconazole (100 mg/day): a double-blind, multicentre study. Randomized comparative medical trial of itraconazole and selenium sulfide shampoo for the remedy of pityriasis versicolor. Repeated-dose pharmacokinetics of an oral solution of itraconazole in infants and kids. First-trimester itraconazole exposure and pregnancy outcome: a potential cohort examine of girls contacting teratology info providers in Italy. Clinical makes use of of the drug 2807 contributes to itraconazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Coadministration of rifampin and itraconazole leads to undetectable levels of serum itraconazole. Itraconazole and hydroxyitraconazole serum concentrations are reduced greater than tenfold by phenytoin. In vitro fungicidal actions of voriconazole, itraconazole, and amphotericin B in opposition to opportunistic moniliaceous and dematiaceous fungi. Cryptococcus neoformansCryptococcus gattii species complex: a global examine of wildtype susceptibility endpoint distributions and epidemiological cutoff values for fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole. In vitro susceptibility to itraconazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole and terbinafine of 100 isolates of Trichophyton rubrum. Beneficial pharmacokinetic interplay between cyclosporine and itraconazole in renal transplant recipients. Clinical apply guideline for the usage of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with most cancers: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. High prevalence of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from high-risk patients. Comparison of oral fluconazole and itraconazole for progressive, nonmeningeal coccidioidomycosis. Adverse effects of antifungal therapies in invasive fungal infections: evaluation and metaanalysis. Breakthrough invasive fungal infections in neutropenic sufferers after prophylaxis with itraconazole. Itraconazole trough concentrations in antifungal prophylaxis with six different dosing regimens utilizing hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin oral resolution or coated-pellet capsules. Antifungal prophylaxis with itraconazole in neutropenic patients with acute leukaemia. In vitro analysis of griseofulvin, ketoconazole, and itraconazole in opposition to varied dermatophytes in Singapore. In vitro activities of permitted and investigational antifungal brokers in opposition to 44 scientific isolates of basidiomycetous fungi. A evaluation of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in superficial and systemic mycoses. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of cyclodextrin itraconazole in pediatric patients with oropharyngeal candidiasis. Safety and efficacy of intermittent remedy with itraconazole in finger- and toenail onychomycosis: a multicentre trial. Pharmacokinetics of itraconazole following oral administration to normal volunteers. A double-blind, randomized study evaluating itraconazole pulse therapy with steady dosing for the therapy of toe-nail onychomycosis.
|
|

